The Setup of the testing environment:
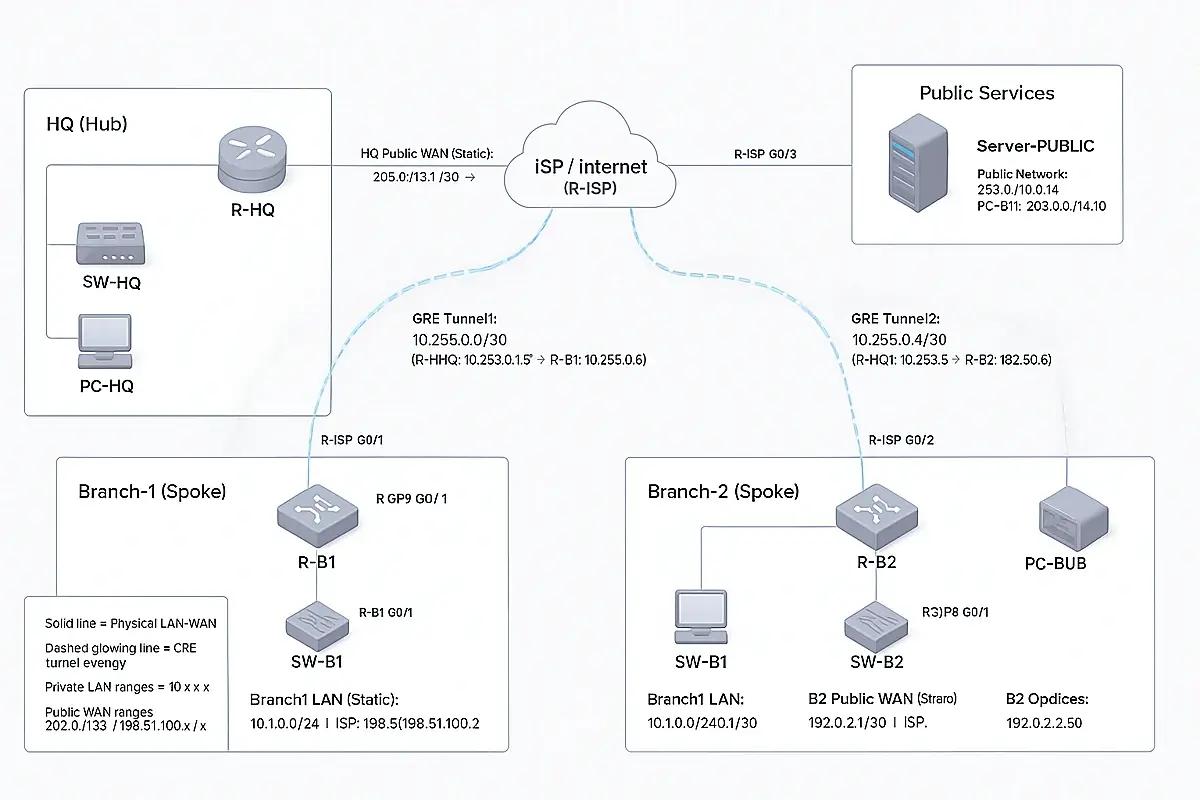
A Network That Turns From Chaos Into a System That Never Falls
HQ + Branches Hub-and-Spoke Design (Connectivity + Security)
1) Goal of the Design
- Connect all branches to HQ so the company works as one network.
- Keep HQ as the central controller (Hub).
- Make the connection secure, stable, and easy to troubleshoot.
- Scale easily: add Branch-3 / Branch-4 / Branch-5 by repeating the same template.
2) Concept: Hub-and-Spoke
- HQ = Hub (the brain)
- Branches = Spokes
- Each branch builds one tunnel to HQ.
- Branch-to-branch communication is not allowed by default (unless HQ permits it).
- Benefits:
- Central control and visibility
- Less complexity than full mesh
- Easier policy enforcement and logging
3) Phase 0: Pre-Checks (Before Any VPN Work)
Objective: ensure WAN and routing are stable (a tunnel cannot be stable on an unstable WAN).
Run on each router/firewall:
show ip interface brief
show ip route
ping <ISP-next-hop>
Expected results:
- WAN interface is up/up
- Default route exists (0.0.0.0/0)
- ISP next-hop replies to ping
4) Phase 1: Build the Overlay (GRE Hub-and-Spoke)
Objective: create a scalable overlay that makes routing between sites simple.
4.1 HQ (Hub) — Create GRE tunnels (template)
Tunnel to Branch-1 (example):
interface tunnel1
ip address <HQ-Tunnel1-IP> <mask>
tunnel source <HQ-WAN-Interface>
tunnel destination <Branch1-Public-IP>
Tunnel to Branch-2 (example):
interface tunnel2
ip address <HQ-Tunnel2-IP> <mask>
tunnel source <HQ-WAN-Interface>
tunnel destination <Branch2-Public-IP>
Repeat this pattern for all branches (Tunnel3, Tunnel4, Tunnel5…).
4.2 Branch (Spoke) — Create GRE tunnel back to HQ (template)
Branch-1 example:
interface tunnel1
ip address <Branch1-Tunnel-IP> <mask>
tunnel source <Branch1-WAN-Interface>
tunnel destination <HQ-Public-IP>
4.3 Routing over GRE (template)
On HQ (routes to branch LANs):
ip route <Branch1-LAN-Subnet> <mask> tunnel1
ip route <Branch2-LAN-Subnet> <mask> tunnel2
On each branch (route to HQ LAN):
ip route <HQ-LAN-Subnet> <mask> <HQ-Tunnel-IP>
4.4 Verification (GRE + Routing)
On HQ:
show interface tunnel1
show interface tunnel2
Expected:
- “Tunnel is up, line protocol is up”
Ping tests:
- From Branch PC → HQ PC
- From HQ PC → Branch PC
5) Phase 2: Secure the Connection (Encryption with IPsec)
Important note:
In real production networks, GRE by itself is not encrypted. We secure it using GRE over IPsec.
5.1 Security Parameters (recommended)
IKE / Phase 1
- Encryption: AES-256
- Integrity: SHA-256
- Diffie-Hellman: Group 14
- Lifetime: 28800 seconds
- Authentication: Pre-Shared Key (PSK) or Certificates
Phase 2 (IPsec / Data)
- AES-256 + SHA-256
- PFS enabled (Group 14)
- Lifetime: 3600 seconds
Stability
- Enable DPD (Dead Peer Detection) / keepalive
5.2 Implementation Steps (vendor-neutral)
- Define “interesting traffic” (what must be encrypted)
- Typically: GRE protocol between HQ public IP and branch public IP
- Configure IKE Phase 1 policy
- Configure IPsec Phase 2 proposal/transform
- Bind IPsec to the WAN interface (crypto map / policy)
- Repeat for each branch peer
5.3 Verification (IPsec)
- Confirm IKE is established
- Confirm IPsec SAs are active
- Confirm encrypted counters increase
- Confirm LAN-to-LAN traffic still works
6) Phase 3: Reduce Attack Surface (Lock Down the WAN)
Objective: allow only VPN-related traffic from known peers.
Typical WAN allow list:
- UDP 500 (IKE)
- UDP 4500 (NAT-T, if used)
- ESP (IP protocol 50)
- GRE (protocol 47) if GRE is used
Everything else is denied.
7) Phase 4: Central Control (HQ is the Brain)
- If the business requires: Branches must not communicate directly
- Enforce via routing and firewall policies:
- Allow Branch → HQ services only
- Deny Branch ↔ Branch traffic unless approved
- Enforce via routing and firewall policies:
You already have:
- WAN IPs working
- GRE tunnels up
- Routing between LANs working
Now we will:
- Encrypt GRE with IPsec (GRE over IPsec)
- (Optional) Lock down WAN inbound with ACL so only VPN traffic is allowed
- Verify with show crypto commands
Step 1 — Verify GRE is UP (quick check)
Run on R-HQ:
show interface tunnel1
show interface tunnel2
Expected:
- Tunnel is up, line protocol is up
Step 2 — Apply IPsec on HQ (R-HQ) to protect both GRE tunnels
✅ Copy/paste on R-HQ:
enable
conf t
! =========================================================
! A) Interesting traffic: encrypt GRE between PUBLIC WAN IPs
! =========================================================
ip access-list extended ACL-GRE-HQ-B1
permit gre host 203.0.113.1 host 198.51.100.1
ip access-list extended ACL-GRE-HQ-B2
permit gre host 203.0.113.1 host 192.0.2.1
! =========================================================
! B) IKE Phase 1 (IKEv1) – Strong settings
! =========================================================
crypto isakmp policy 10
encr aes 256
hash sha256
authentication pre-share
group 14
lifetime 28800
! If Packet Tracer rejects sha256, use SHA instead:
! crypto isakmp policy 10
! encr aes 256
! hash sha
! authentication pre-share
! group 14
! lifetime 28800
! DPD / Keepalive (stability)
crypto isakmp keepalive 10 periodic
! Pre-shared key per branch peer
crypto isakmp key vpnHQ123 address 198.51.100.1
crypto isakmp key vpnHQ123 address 192.0.2.1
! =========================================================
! C) IKE Phase 2 (IPsec)
! =========================================================
crypto ipsec transform-set TS-GRE esp-aes 256 esp-sha-hmac
mode tunnel
! =========================================================
! D) Crypto Map – One entry per branch
! =========================================================
crypto map CMAP-IPSEC 10 ipsec-isakmp
description GRE_over_IPsec_to_Branch1
set peer 198.51.100.1
set transform-set TS-GRE
set pfs group14
set security-association lifetime seconds 3600
match address ACL-GRE-HQ-B1
crypto map CMAP-IPSEC 20 ipsec-isakmp
description GRE_over_IPsec_to_Branch2
set peer 192.0.2.1
set transform-set TS-GRE
set pfs group14
set security-association lifetime seconds 3600
match address ACL-GRE-HQ-B2
! =========================================================
! E) Apply IPsec to HQ WAN interface (WAN = g0/1 in your doc)
! =========================================================
interface g0/1
crypto map CMAP-IPSEC
end
wr
Step 3 — Apply IPsec on Branch1 (R-B1)
✅ Copy/paste on R-B1:
enable
conf t
! Encrypt GRE between Branch1 WAN and HQ WAN
ip access-list extended ACL-GRE-B1-HQ
permit gre host 198.51.100.1 host 203.0.113.1
crypto isakmp policy 10
encr aes 256
hash sha256
authentication pre-share
group 14
lifetime 28800
! If sha256 is not supported in your PT IOS, use SHA:
! crypto isakmp policy 10
! encr aes 256
! hash sha
! authentication pre-share
! group 14
! lifetime 28800
crypto isakmp keepalive 10 periodic
crypto isakmp key vpnHQ123 address 203.0.113.1
crypto ipsec transform-set TS-GRE esp-aes 256 esp-sha-hmac
mode tunnel
crypto map CMAP-IPSEC 10 ipsec-isakmp
description GRE_over_IPsec_to_HQ
set peer 203.0.113.1
set transform-set TS-GRE
set pfs group14
set security-association lifetime seconds 3600
match address ACL-GRE-B1-HQ
interface g0/1
crypto map CMAP-IPSEC
end
wr
Step 4 — Apply IPsec on Branch2 (R-B2)
✅ Copy/paste on R-B2:
enable
conf t
! Encrypt GRE between Branch2 WAN and HQ WAN
ip access-list extended ACL-GRE-B2-HQ
permit gre host 192.0.2.1 host 203.0.113.1
crypto isakmp policy 10
encr aes 256
hash sha256
authentication pre-share
group 14
lifetime 28800
! If sha256 is not supported in your PT IOS, use SHA:
! crypto isakmp policy 10
! encr aes 256
! hash sha
! authentication pre-share
! group 14
! lifetime 28800
crypto isakmp keepalive 10 periodic
crypto isakmp key vpnHQ123 address 203.0.113.1
crypto ipsec transform-set TS-GRE esp-aes 256 esp-sha-hmac
mode tunnel
crypto map CMAP-IPSEC 10 ipsec-isakmp
description GRE_over_IPsec_to_HQ
set peer 203.0.113.1
set transform-set TS-GRE
set pfs group14
set security-association lifetime seconds 3600
match address ACL-GRE-B2-HQ
interface g0/1
crypto map CMAP-IPSEC
end
wr
Step 5 — Bring the VPN up (generate “interesting traffic”)
IPsec will NOT fully establish until GRE traffic starts flowing.
From PC-Branch1, ping PC-HQ:
ping 10.0.0.50
From PC-Branch2, ping PC-HQ:
ping 10.0.0.50
Do 2–3 pings if the first fails.
Step 6 — Verify IPsec is working (must check these)
On HQ (R-HQ):
show crypto isakmp sa
show crypto ipsec sa
Expected:
- ISAKMP state shows something like QM_IDLE
- IPsec SA counters (pkts encaps / decaps) increase
On Branch1 (R-B1) and Branch2 (R-B2):
show crypto isakmp sa
show crypto ipsec sa
Step 7 (Optional but recommended) — Lock down WAN inbound with ACL
This prevents random traffic from hitting your WAN interface and allows only VPN traffic from the known peers.
7.1 HQ WAN ACL (apply inbound on HQ WAN g0/1)
✅ Copy/paste on R-HQ:
enable
conf t
ip access-list extended WAN-IN
! Allow IKE from branches to HQ
permit udp host 198.51.100.1 host 203.0.113.1 eq 500
permit udp host 192.0.2.1 host 203.0.113.1 eq 500
! Allow ESP (IP protocol 50)
permit esp host 198.51.100.1 host 203.0.113.1
permit esp host 192.0.2.1 host 203.0.113.1
! Allow GRE (protocol 47) – because we run GRE over IPsec
permit gre host 198.51.100.1 host 203.0.113.1
permit gre host 192.0.2.1 host 203.0.113.1
! Optional: allow ping to WAN for testing
permit icmp any host 203.0.113.1
deny ip any any log
interface g0/1
ip access-group WAN-IN in
end
wr
7.2 Branch1 WAN ACL (inbound on Branch1 WAN g0/1)
✅ Copy/paste on R-B1:
enable
conf t
ip access-list extended WAN-IN
permit udp host 203.0.113.1 host 198.51.100.1 eq 500
permit esp host 203.0.113.1 host 198.51.100.1
permit gre host 203.0.113.1 host 198.51.100.1
permit icmp any host 198.51.100.1
deny ip any any log
interface g0/1
ip access-group WAN-IN in
end
wr
7.3 Branch2 WAN ACL (inbound on Branch2 WAN g0/1)
✅ Copy/paste on R-B2:
enable
conf t
ip access-list extended WAN-IN
permit udp host 203.0.113.1 host 192.0.2.1 eq 500
permit esp host 203.0.113.1 host 192.0.2.1
permit gre host 203.0.113.1 host 192.0.2.1
permit icmp any host 192.0.2.1
deny ip any any log
interface g0/1
ip access-group WAN-IN in
end
wr
If you still need open WAN access for other services, do not apply these ACLs or customize them.
Step 8 — Troubleshooting (fast fixes)
- A) If hash sha256 fails
Use hash sha on ALL routers (HQ + branches).
- B) If IPsec doesn’t come up
Check:
show crypto isakmp sa
show crypto ipsec sa
Then generate traffic again (ping from branch to HQ).
- C) If you applied WAN ACL and VPN stopped
Remove the ACL temporarily:
conf t
interface g0/1
no ip access-group WAN-IN in
end
